What can we do?
At Erasmus MC, medical care for infectious diseases is in the hands of a team of specialised doctors and nurses at the Internal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Department.
You have been exposed to potentially infected blood or other potentially contaminated body fluids (we call this 'risky exposure'). This may have introduced pathogens into your blood, such as the hepatitis B virus, the hepatitis C virus or the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Hepatitis B and C viruses can cause inflammation of the liver. HIV can cause a serious immune disorder. Medication can reduce the risk of HIV infection.
Immunoglobins
You will be given a single injection of immunoglobulins which will provide immediate protection against any hepatitis B virus that may be present. You may need another injection of immunoglobulins after one month.
Active vaccination
Active vaccination involves three injections of the hepatitis B vaccine. This causes the body to produce antibodies (defence) against the virus. The first injection should be given within a week of the risky exposure. You will receive the second vaccination 1 month later and the third 6 months after the first. You can get these vaccinations through the Erasmus MC Health Service, the Municipal Health Service (GGD), the HIV consultant or your GP.
You have been exposed to potentially infected blood or other potentially contaminated body fluids (we call this 'risky exposure'). This may have introduced pathogens into your blood, such as the hepatitis B virus, the hepatitis C virus or the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Hepatitis B and C viruses can cause inflammation of the liver. HIV can cause a serious immune disorder. Medication can reduce the risk of HIV infection.
Hepatitis B
If you have had a full vaccination against hepatitis B in the past and have built up sufficient antibodies, you are protected against this infection. If not, we can reduce the risk of infection with the virus by administering immunoglobulins (special antibodies against the hepatitis B virus) or a vaccine (active vaccination). Your attending physician will decide which treatment is right for you:Immunoglobins
You will be given a single injection of immunoglobulins which will provide immediate protection against any hepatitis B virus that may be present. You may need another injection of immunoglobulins after one month.
Active vaccination
Active vaccination involves three injections of the hepatitis B vaccine. This causes the body to produce antibodies (defence) against the virus. The first injection should be given within a week of the risky exposure. You will receive the second vaccination 1 month later and the third 6 months after the first. You can get these vaccinations through the Erasmus MC Health Service, the Municipal Health Service (GGD), the HIV consultant or your GP.
Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, at present, it is not yet possible to prevent infection with the hepatitis C virus after risky exposure. However, should you develop a hepatitis C infection, treatment at an early stage is possible.HIV
To reduce the risk of infection with HIV, you can take medication. This treatment is called Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP).Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
What is Post Exposure Prophylaxis?
Post = afterExposure = a situation in which HIV has the chance to enter a person's body
Prophylaxis = a treatment aimed at preventing infection
- PEP can help to prevent a person from becoming infected with HIV
- PEP is a 4-week course of HIV medication
- PEP should be started as soon as possible after risky exposure (up to a maximum of 72 hours)
- PEP has side effects
Whether you need PEP depends on the risk you face:
- Do you know if the needle you pricked yourself with was used by someone who is HIV-positive?
- Is the partner with whom you had sex HIV-positive? Or is this unknown?
- Receptive sex (anal/vaginal) is riskier than insertive sex (anal/vaginal), which in turn is riskier than oral sex.
- With blow jobs, the risk is even lower if no semen enters the mouth. If semen does enter the mouth, the risk of infection is greater if it is swallowed.
- You cannot catch HIV from someone giving you oral sex. PEP is then unnecessary.
If the source is HIV-positive, the viral load (the amount of virus) in their blood also plays a role.
- If the viral load of the source is undetectable, the risk is very small. The higher the viral load, the higher the risk of infection.
- If the HIV-positive source has another STI, then the risk of HIV transmission is probably also higher.
- If the PEP applicant has an STI, then their susceptibility to HIV is also likely to be higher.
The procedure
Your attending physician will decide whether you are eligible for PEP. The treatment must be started as soon as possible but, in any case, within 72 hours after the risk.The accident took place during office hours:
The staff at the emergency room or health and safety services will make an urgent appointment for you at the Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic on the same day.
The accident took place outside office hours:
The emergency department will give you an emergency kit with PEP medication (HIV inhibitors) for 5 days. In total, you have to take HIV inhibitors for 28 days.
You should make an appointment at the Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic at Erasmus MC on the first workday after the incident. To make an appointment, please contact us (see 'Contact' - 'Emergency' below).
At the Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic, the internist/infectious disease specialist and HIV nurse consultant will provide you with information about the medication, intake and possible side effects. You can ask them all your questions and they will be happy to help. You will be given a number of follow-up appointments and a prescription for the necessary medication.
The medication
You start with a combination of HIV inhibitors that you have to take for 28 days. This combination always consists of at least 3 active medicines. Sometimes 2 medicines are combined in 1 tablet. The internist/infectious disease specialist will decide which combination of HIV inhibitors you will receive. In most cases, this is a combination of Truvada® and Tivicay® (see table). You take Truvada® and Tivicay® together once a day at a fixed time.You must take the medicines at the same time every day (for instance, every day at 8.00 o'clock).
Because you need to take the first dose of the medicines as soon as possible after the incident (in the emergency room), you may need to take the second dose after less than 24 hours. This is not a problem if it is only this once. Choose a time that suits you so that you can take the medicines consistently for 28 days.
Important:
Take the medicine consistently.
Take the correct dosage.
Do not skip any doses!
The HIV nurse consultant will discuss the dosage schedule with you during your appointment at the Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic. They will also advise you about the PEP medication.
Dosage and possible side effects
Truvada® (Tenofovird isoproxil / Emtricitabine)
Truvada® is a blue or green tablet consisting of 245 mg Tenofovir disoproxil and 200 mg Emtricitabine. Truvada®. Store the tablets at room temperature. Protect the tablets from moisture, freezing and heat. The dose is 1 tablet once a day. You can take Truvada® with or without a meal. The time between taking the tablets is always 24 hours.Please note: take the medicines consistently, take the correct dosage and don't skip any doses.
Possible side-effects of Truvada®
Possible side effects of Truvada® are headaches, dizziness, diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea and kidney dysfunction.
Tivicay® (Dolutegravir)
Tivicay® is a pale yellow tablet containing 50 mg of Dolutegravir. Store the tablets at room temperature. Protect the tablets from moisture, freezing and heat. The dose is 1 tablet once a day. You can take Tivicay® with or without a meal. The time between taking the tablets is always 24 hours.Please note: take the medicines consistently, take the correct dosage and don't skip any doses.
Possible side-effects of Tivicay®
Possible side effects of Tivicay® are diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, sleeping problems and mood problems.
| Brand name | Substance | Daily dose |
| Truvada® | Combination of 2 substances/medicines in 1 tablett: - Tenofovirdisoproxil 245 mg - Emtricitabine 200 mg | 1 tablet a day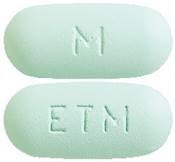 or  |
| Tivicay® | Dolutegravir 50 mg | 1 tablet once a day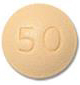 |
Interaction with your other medication
There are medicines that you should not take together with Truvada® or Tivicay® or that require a different dose of one of the medicines. You must inform your physician about all the medicines you are taking or plan to take, including those not prescribed by a doctor.Please note: St. John's wort, multivitamins, iron tablets, antacids and grapefruit juice also influence the effect of Truvada® and Tivicay®. Do not take them during the treatment.
What if you forget your medication?
If you have forgotten to take your medication, take it immediately! You can then resume your normal schedule. It doesn't matter when you realise you have forgotten to take the medication, but it won't do any good to take a double dose to make up for a forgotten one. So if you only realise you forgot a dose when you need to take the tablets again, do not take a double dose.Nausea and vomiting
If you vomit after taking the medicines, you may have to take them again. The rules for this are:You took the medication without food:
- You vomit within 1 hour of taking the medication → take it again.
- You vomit at least 1 hour after taking the medication → do not take it again.
- There are remains of medication in the vomit → always take it again.
- You vomit within 3 hours of taking the medication → take it again.
- You vomit at least 3 hours after taking the medication → do not take it again.
- There are remains of medication in the vomit → always take it again.
Safe sex
An important consequence of taking PEP is that you must have safe sex (including with your regular partner) until you have tested HIV negative after 4 months. So always use a condom for sex. This applies to oral, vaginal and anal sex.
For more information about safe sex, go to: www.soaaids.nl
and www.ggdrotterdamrijnmond.nl.
Depending on the cause of the possible infection, it may be wise to have yourself checked for other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This can be done at the GGD or during the Venim (STI) consultation hours at the Erasmus MC.
For more information, go to:
www.ggdrotterdamrijnmond.nl
For more information about safe sex, go to: www.soaaids.nl
and www.ggdrotterdamrijnmond.nl.
Depending on the cause of the possible infection, it may be wise to have yourself checked for other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This can be done at the GGD or during the Venim (STI) consultation hours at the Erasmus MC.
For more information, go to:
www.ggdrotterdamrijnmond.nl
HIV testing, blood samples and follow-up appointments
From the moment you start taking the PEP medication, we will supervise your intake at the Erasmus MC Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic. After your first appointment with the physician, the HIV/Aids nurse consultant will make follow-up appointments for you.
Blood samples and agreements
Blood samples and agreements
- Before you start the PEP medication, we will take a blood sample from you that we can later test for HIV if required.
- 4 months after the accident (3 months after stopping the PEP), we will take another blood sample from you at the Erasmus MC for testing for HIV and, on indication, syphilis, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- You will be given the results one week later during a telephone appointment with the internist/infectious disease specialist.
Questions
If you have any questions or problems with, for example, side effects from the medication, ask one of the nurse consultants. They will be happy to help. You can also always contact the Infectious Diseases Outpatient Clinic.
Contact
If you have a question or want to make an appointment:
- Monday to Friday from 08.00 a.m. to 11.00 a.m.: contact the infectious disease consultants via +31 10 703 57 37 (telephone consultation hours)
- Monday to Friday from 11.00 a.m. to 4.30 p.m.: contact the outpatient clinic assistant via +31 10 704 05 71
In case of emergency in the evening, night or weekend, please contact +31 10 704 0 704. This is the general phone number of the Erasmus MC. Ask for the attending medical assistant for internal medicine.